
Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) is a responsible attitude and respectful of life, after all, PPE guarantees daily that many workers perform their tasks safely. However, in addition, the equipment ensures well-being and avoids possible damage to health, caused by adversity, as is the case, for instance, of excess solar radiation – a subject that we will address in this post from JGB.
Problems caused by solar radiation
The sun is responsible for ultraviolet radiation, classified into three types: UVA, UVB and b. Of these, UVA and UVB are the ones that can cause health problems when employees are under sunlight without proper protection. And that goes for any time of the year, regardless of temperature, season and weather, since solar radiation is present even on cloudy and rainy days.
UVA rays, although they do not cause burns, they are able to penetrate the deeper layers of the skin and damage the collagen and elastin fibers, causing premature aging. UVB rays, in turn, cause redness of the skin and burns.
In addition to these complications, overexposure to these rays can lead to the appearance of freckles and spots, increasing the risk of developing cancer and related diseases, without forgetting damage to the eyes, such as cataracts and blindness. That is why it is essential that employees whose work requires exposure to the sun have adequate protection. This is where personal protective equipment comes in.
The role of textiles
With microcapsules used and prepared in the spinning of fibers, textiles can be an intrinsically barrier against radiation. The protective action preserves the skin, as it may be seen in the figure below:
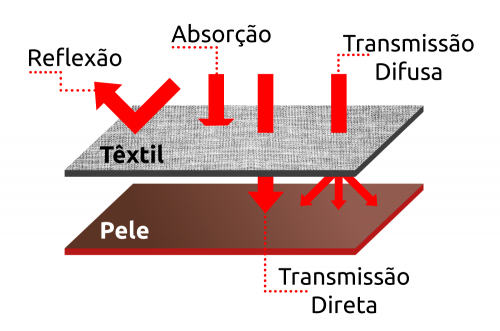
Source: Centro Tessile Cotoniero e Abbigliamento S.p.A.
The fabrics used in daily life do not block UVA and UVB rays. That is, the part of the skin that is covered also receives solar radiation, but it is possible to protect yourself using Texion® C and Texion® S fabrics.
According to the principle of ultraviolet protection, a technology must block at least 97.5% of UV rays to be level 40, 50 or +50. Products over 40 are classified as having excellent protection against ultraviolet rays. According to reports 0193/17 and 0197/17, Texíon® C and Texíon® S are at the +50 level. That is, they are considered excellent protection! The opinion is from the SENAI CETIQT laboratory, which follows the AS / NZS 4399: 1996 standard, which establishes the requirements for determining the ultraviolet protection factor of sunscreen fabrics, clothing and other items of personal clothing used in close proximity to the skin.

Remember that the good security technician must be aware of these details and provide the best solution for the work team! Contact JGB to learn more about Texíon® C and Texíon® S. Questions about PPE? Contact us! We are available to serve you!